Merging and splitting data#
In this chapter, you will learn how to merge and split data, and in what cases it might be useful to perform these operations.
Merging data#
In some cases, you might need to merge (combine) and process data from different sources.
Merging data can involve:
- Creating one data set from multiple sources.
- Synchronizing data between multiple systems. For example, removing duplicate data, or updating data in one system when it changes in another.
One-way vs. two-way sync
In a one-way sync, data is synchronized in one direction. One system serves as the single source of truth. When information changes in that main system, it automatically changes in the secondary system; but if information changes in the secondary system, the changes are not reflected in the main system.
In a two-way sync, data is synchronized in both directions (between both systems). When information changes in either of the two systems, it automatically changes in the other one as well.
This blog tutorial explains how to sync data one-way and two-way between two CRMs.
In n8n, you can merge data from two different nodes using the Merge node, which provides several merging modes:
- Append
- Keep Key Matches
- Merge By Index
- Merge By Key
- Multiples
- Pass-through
- Remove Key Matches
- Wait
Notice that three of these modes require a key (Merge By Key, Keep Key Matches, Remove Key Matches). This key represents a common property between the two data sources, based on which the data can be merged. In the Merge node, they are called Property Input 1 and Property Input 2.
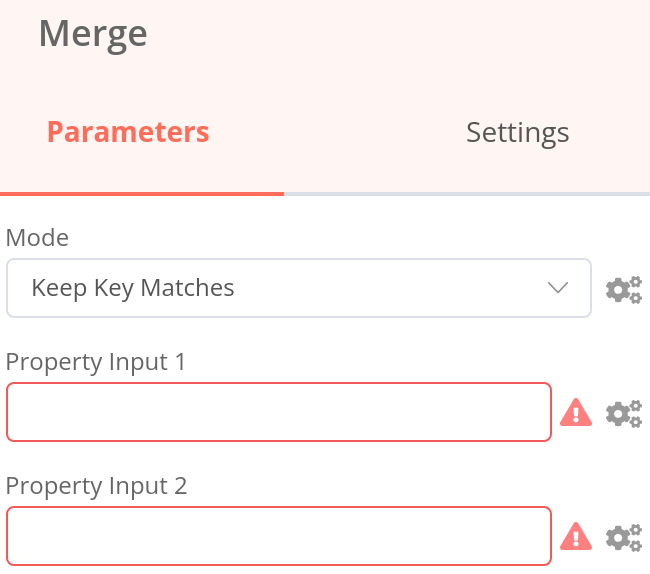
Property Input in dot notation
If you want to reference nested values in the Merge node parameters Property Input 1 and Property Input 2, you need to enter the property key in dot-notation format (as text, not as an expression).
Note
You can also find the Merge node under the alias Join. This might be more intuitive if you're familiar with SQL joins.
Exercise#
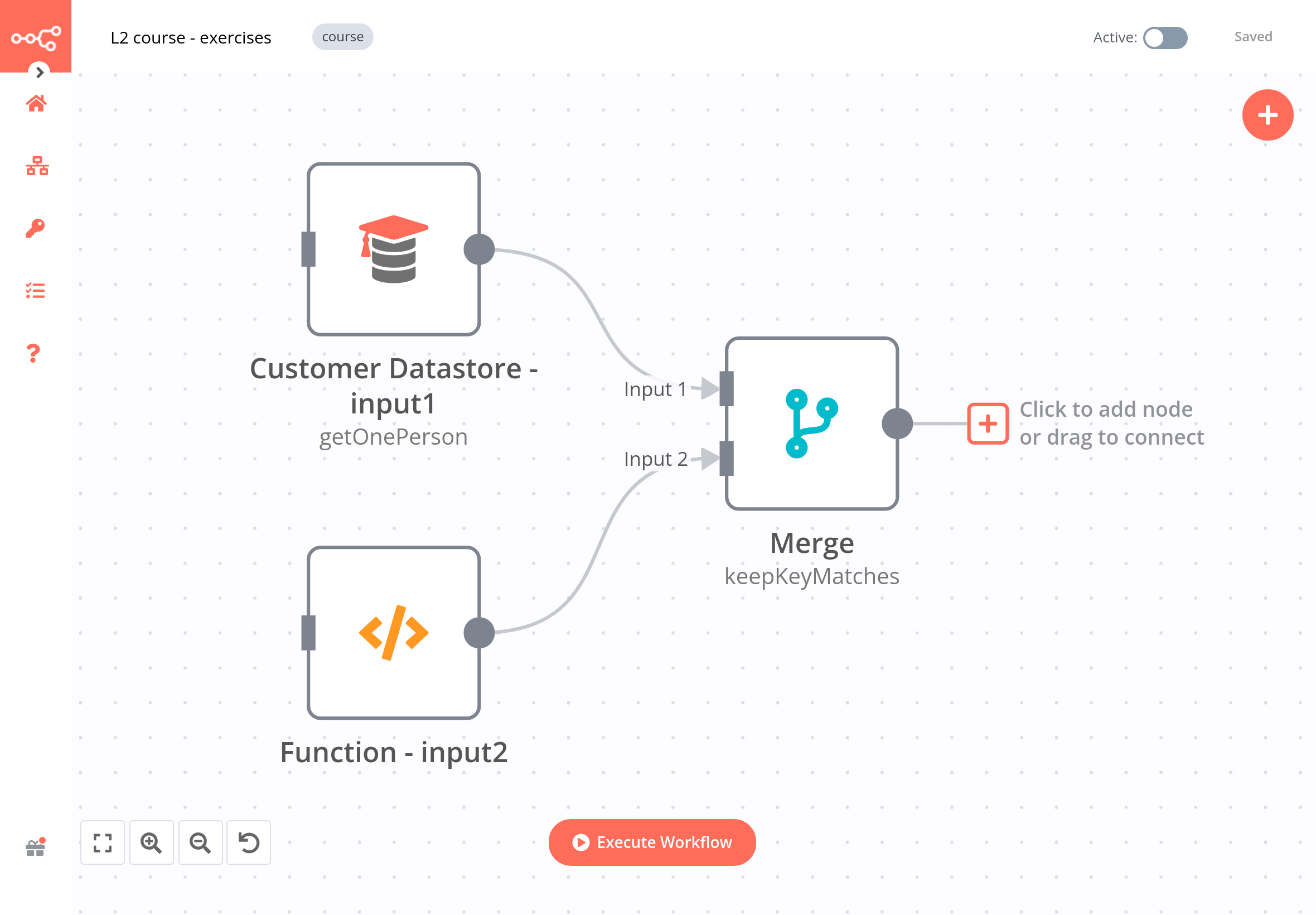
Build a workflow that merges data from the Customer Datastore node and Code node.
- Add a Merge node that takes Input 1 from a Customer Datastore node and Input 2 from a Code node.
- In the Customer Datastore node, run the operation Get All People.
- In the Code node, create an array of two objects with three properties:
name,language, andcountry, where the propertycountryhas two sub-propertiescodeandname. Fill out the values of these properties with the information of two characters from the Customer Database. For example, Jay Gatsby's language would be English and country name would be United States. - In the Merge node, try out different merge modes.
Show me the solution
The workflow for this exercise looks like this:
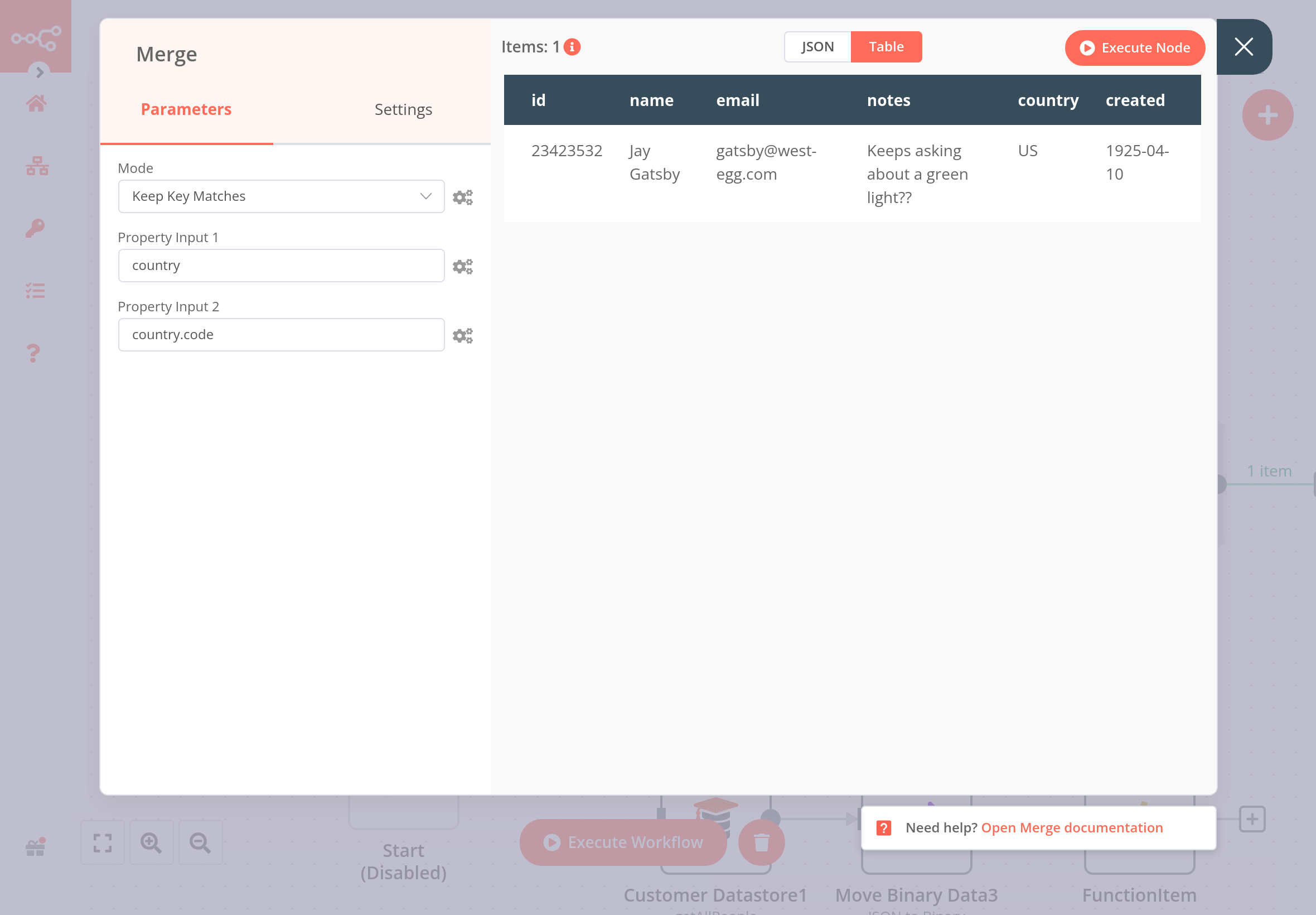
If you merge data with the option Keep Key Matches using the country code as the common key, the result should look like this:
Looping#
In some cases, you might need to perform the same operation on each element of an array / each data item (for example sending a message to every contact in your address book). In technical terms, you need to iterate through the data (with loops).
n8n handles this repetitive processing automatically, as the nodes run once for each item, so you don't need to build loops into your workflows. However, there are some exceptions of nodes and operations for which you need to build a loop into your workflow.
To create a loop in an n8n workflow, you need to connect the output of one node to the input of a previous node, and add an IF node to check when to stop the loop.
Splitting data in batches#
If you need to process large incoming data, execute the Code node multiple times, or avoid API rate limits, it's best to split the data into batches (groups) and process these batches. You can do this with the Split in Batches node. This node splits input data into a specified batch size and, with each iteration, returns a predefined amount of data.
Execution of Split in Batches node
The Split In Batches node stops executing after all the incoming items get divided into batches and passed on to the next node in the workflow, so it is not necessary to add an IF node to stop the loop.
Exercise#
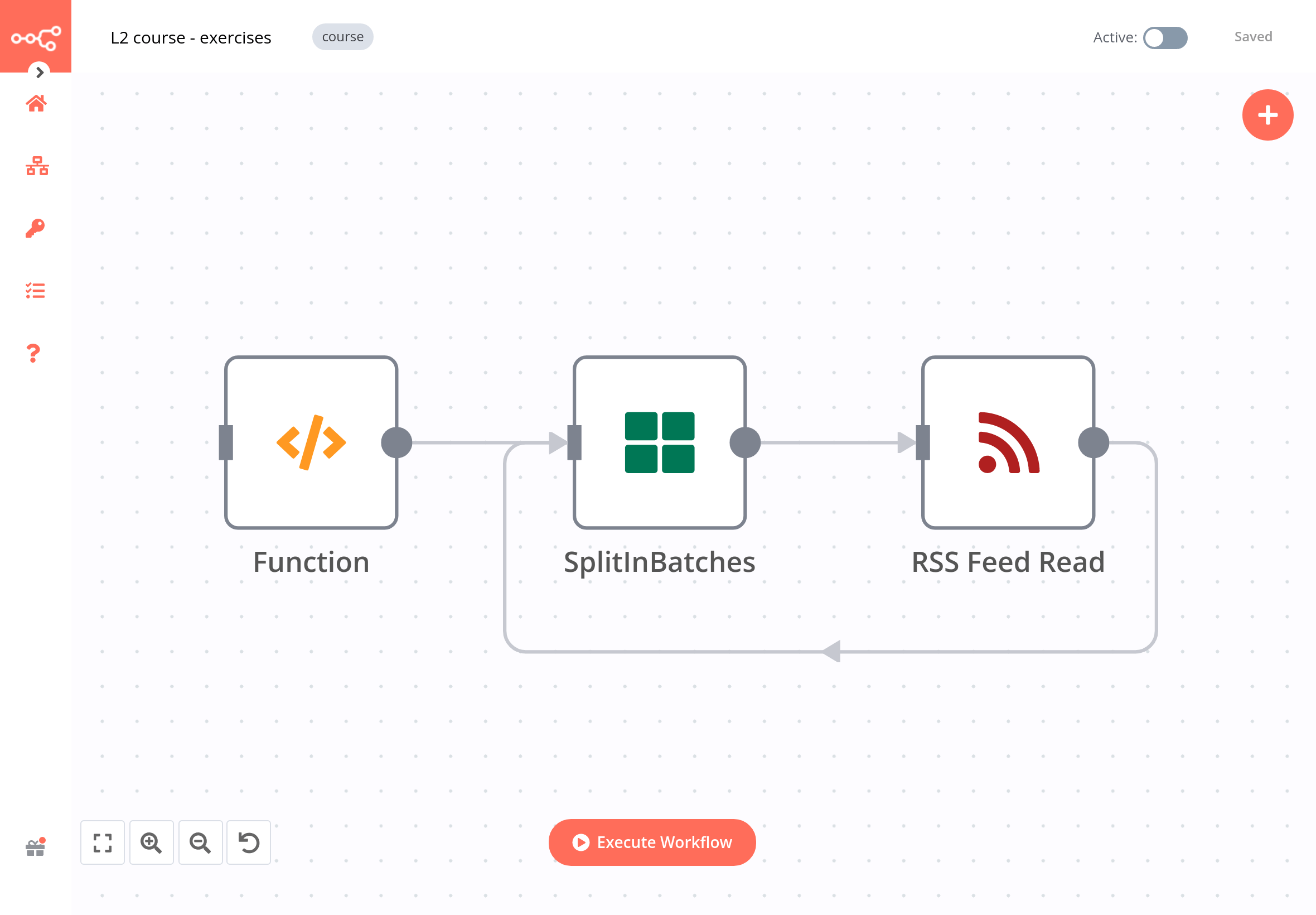
Build a workflow that reads the RSS feed from Medium and dev.to. The workflow should consist of three nodes:
- A Code node that returns the URLs of the RSS feeds of Medium (
https://medium.com/feed/n8n-io) and dev.to (https://dev.to/feed/n8n) - A Split In Batches node with
Batch Size: 1, that takes in the inputs from the Code node and RSS node and iterates over the items. - An RSS Read node that gets the URL of the Medium RSS feed, passed as an expression:
{{$node["SplitInBatches"].json["url"]}}. The RSS Read node is one of the exception nodes which processes only the first item it receives, so the Split in Batches node is necessary for iterating over multiple items.
Show me the solution
The workflow for this exercise looks like this:
To check the configuration of the nodes, you can copy-paste the JSON code of the workflow:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 | |